Ophthalmology Outcomes
Pediatric and Adult Strabismus Surgery
Ophthalmologists with joint appointments at Boston Children’s Hospital and the Mass Eye and Ear Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus Service offer subspecialized medical and surgical care for the full spectrum of pediatric ophthalmic disorders, including strabismus (in children and adults), cataract, anterior segment disease, oculoplastic surgery, neuro-ophthalmology, ocular trauma, ocular oncology, inherited retinal degenerations, and vitreoretinal surgery.
Pediatric and Adult Strabismus Surgery
Strabismus surgery is the most commonly performed ophthalmic procedure in children. This type of surgery is also performed on adults with new or previously existing ocular misalignment. Recession and resection procedures are typically performed for horizontal misalignment (esotropia and exotropia); other approaches include tuck, loop myopexy and transposition procedures for horizontal, vertical and torsional forms of misalignment. Adjustable sutures are used routinely in children and adults. The service has a high rate of quaternary referrals from other pediatric and strabismus specialists to manage the rarest and most complex cases, with nearly half of all patients treated having undergone prior strabismus surgery.
Distribution of Strabismus Patients by Age and Surgical Approach
The Strabismus Service at Boston Children’s Hospital offers comprehensive evaluation and treatment for children and adults with strabismus. In 2023, 807 total strabismus procedures were performed at Boston Children’s Hospital, Massachusetts Eye and Ear, the University of Massachusetts, and other Harvard affiliates. These procedures addressed misalignments that were horizontal, vertical, and torsional in nature.
Distribution of Risk Factors in Strabismus Patients
Of the 807 total strabismus surgeries performed in 2023, 393 patients presented with risk factors associated with a worse surgical outcome. Of these 393 patients with risk factors, the most common risk factors were a history of prior strabismus surgery (46.6%), divergence insufficiency (8.4%), and 4th nerve palsy (7.1%). Other common risk factors were 6th nerve palsy, cerebral palsy, Duane syndrome, heavy eye syndrome, 3rd nerve palsy, developmental delays, premature birth, craniofacial disorders, high myopia, brain tumor, Down Syndrome, and nystagmus.
Goal-Determined Outcomes
Since the desired surgical outcome depends on the primary indication for surgery, we used a goal-determined methodology to assess outcomes of horizontal strabismus surgery.1,2 The reported outcomes include procedures performed by ophthalmologists with joint appointments at Boston Children’s Hospital and the Mass Eye and Ear Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus Service. Procedures performed by the Mass Eye and Ear Adult Neuro-Ophthalmology service are not included in this analysis.
Before and After Horizontal Strabismus Surgery
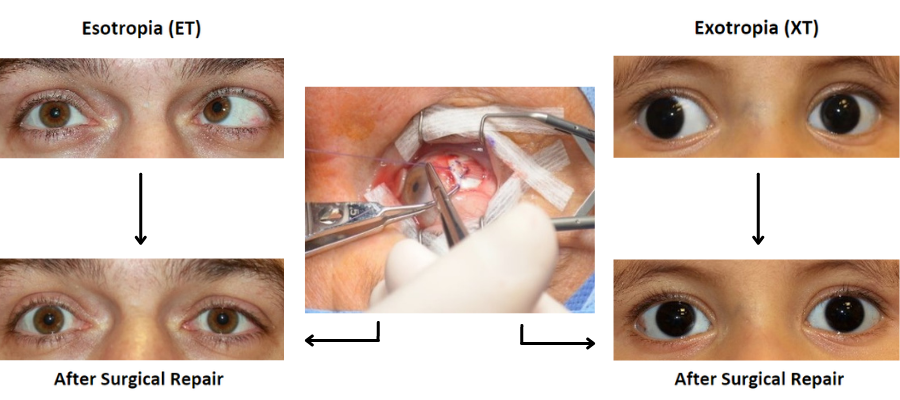
Surgical Outcomes for Horizontal Strabismus
The analysis shown below includes all patients treated in 2023 for horizontal strabismus without exclusion, and therefore facilitates stratification based on the presence or absence of risk factors (ophthalmic or systemic) that might impact results
Exotropia Outcomes Stratified by Goal
In 2023, of the 807 total strabismus procedures, 199 patients with exotropia underwent strabismus surgery and completed post-operative evaluation. Of these, 33 patients had surgery to preserve or restore binocular vision (binocular potential), 138 had reconstructive surgery for normalizing eye contact, and 25 had surgery to eliminate double vision (diplopia). Outcomes criteria for enhancing binocular potential are the most stringent. Due to the small number, the three procedures performed to resolve torticollis were excluded from this analysis.
Exotropia Outcomes Stratified by Risk Factors
Of the 199 patients treated for exotropia referenced above, 109 had associated risk factors, and 90 had no associated risk factors. Risk factors included: bilateral vision limitation (e.g. albinism), conditions resulting in hyper- or hypotonia, craniofacial anomalies, 3rd nerve palsy, 4th nerve palsy, prior strabismus surgery, Duane syndrome, prior surgery for retinal detachment, Graves’ orbitopathy, antecedent orbital trauma with or without orbital fracture, congenital fibrosis of the extraocular muscles, and simultaneous surgery for nystagmus or vertical strabismus. In the presence of these complicating conditions, 88.1% of strabismus surgeries for exotropia with an associated risk factor and 86.7% without additional risk factors had an excellent or good outcome as defined by the metrics published by Chang et al.1
Esotropia Outcomes Stratified by Goal
In 2023, of the 807 total strabismus procedures, 302 patients with esotropia underwent strabismus surgery and completed post-operative evaluation. Of these, 83 patients had surgery to restore binocular vision (binocular potential), 114 had reconstructive surgery for normalizing eye contact, and 96 had surgery to eliminate double vision (diplopia). Four procedures performed to resolve torticollis were excluded from this analysis due to the small number.
Esotropia Outcomes Stratified by Risk Factors
Of the 302 patients treated for esotropia referenced above, 131 had associated risk factors and 171 had no associated risk factors. Risk factors included; bilateral vision limitation (e.g. albinism, cataracts, etc.), conditions resulting in hyper- or hypotonia, craniofacial anomalies, 4th nerve palsy, 6th nerve palsy, Duane syndrome, prior strabismus surgery, prior surgery for retinal detachment, Graves’ orbitopathy, antecedent orbital trauma with or without orbital fracture. Despite these complicating conditions, 82.4% of strabismus surgeries for esotropia with an associated risk factor and 93.0% without additional risk factors had excellent or good outcomes as defined by the metrics published by Ehrenberg et al.1
Scleral Perforation During Strabismus Surgery
Scleral perforation is a rare, complication of strabismus surgery, typically occurring during reattachment of eye muscles to the globe. Globe perforation increases the risk of retinal detachment and endophthalmitis . Of the 807 total strabismus procedures performed in 2023, there were zero reported cases (0.0%) of scleral perforation.
Infection Within 30 Days of Surgery
Intra- or extraocular surgery may be complicated by infection in the form of orbital cellulitis, endophthalmitis, sub-Tenon’s space abscess, subconjunctival abscess, subconjunctival sterile abscess, and cellulitis.
In calendar year 2023, of the 807 strabismus surgery procedures performed, there were no post-operative infections (0.0%) within 30 days of surgery.
There were also no post-operative infections for pediatric cataract and ptosis surgery procedures in calendar year 2023, which has been consistent since reporting began in 2013.5-8
Read More
Goal-Deterined Outcomes
1. Ehrenberg M, Nihalani BR, Melvin P, Cain CE, Hunter DG, Dagi LR. Goal-determined metrics to assess outcomes of esotropia surgery. J AAPOS 2014; 18(3): 211-216.
2. Chang YH, Melvin P, Dagi LR. Goal-determined metrics to assess outcomes of exotropia surgery. J AAPOS 2015; 19: 304-310.
Exotropia Outcomes Stratified by Risk Factors
1. Chang YH, Melvin P, Dagi LR. Goal-determined metrics to assess outcomes of exotropia surgery. J AAPOS 2015; 19: 304-310.
Esotropia Outcomes Stratified by Risk Factors
1. Ehrenberg M, Nihalani BR, Melvin P, Cain CE, Hunter DG, Dagi LR. Goal-determined metrics to assess outcomes of esotropia surgery. J AAPOS 2014; 18(3): 211-216.
Scleral Perforation During Strabismus Surgery
1. Bradbury JA. What information can we give to the patient about the risks of strabismus surgery. Eye (Lond) 2015; 29(2): 252-257.
2. Awad AH, Mullaney PB, AI-Hazmi A, et al. Recognized globe perforation during strabismus surgery: incidence, risk factors, and sequelae. J AAPOS 2000; 4(3): 150-153.
3. Morris RJ, Rosen PH, Fells P. Incidence of inadvertent globe perforation during strabismus surgery. Br J Ophthalmol 1990; 74(8): 490-493.
Infection Within 30 Days After Surgery
1. Ing MR. Infection following strabismus surgery. J Ophthalmic Nurs Technol 1991; 10(5): 211-214.
2. Bradbury JA. What information can we give to the patient about the risk of strabismus surgery. Eye (Lond) 2015; 29(2): 252-257.
3. Brenner C, Ashwin M, Smith D, et al. Sub-Tenon's space abscess after strabismus surgery. J AAPOS 2009; 13(2): 198-199.
4. Bradbury JA, Taylor RH. Severe complications of strabismus surgery. J AAPOS 2013; 17(1): 59-63.
5. Haripriya A, Chang DF, Reena M, et al. Complication rates of phacoemulsification and manual small-incision cataract surgery at Aravind Eye Hospital. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2012; 38(8): 1360-1369.
6. Sharma N, Pushker N, Dada T, et al. Complications of pediatric cataract surgery and intraocular lens implantation. J Cataract Refract Surg.1999; 25(12): 1585-1588.
7. Pandey SK, Wilson ME, Trivedi RH, et al. Pediatric cataract surgery and intraocular lens implantation: current techniques, complications, and management. Int Ophthalmol Clin 2001; 41(3): 175-196.
8. Lee EW, Holtebeck AC, Harrison AR. Infection rates in outpatient eyelid surgery. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg 2009; 25(2): 109-110.

